This new ISS report: “Corporates Bolster Their Defenses Amid Growing Cyber Risk” benchmarks cybersecurity related disclosure among the S&P 500 and the Russell 3000 (excluding the S&P 500) (“R3000”) with reference to ISS’s information security GovernanceQuality Score factors (purportedly signifying strong cyber risk management practices) and prior year disclosure practices.
Key takeaways include:
Cyber security training (Q411)
- The vast majority of S&P 500 and R3000 companies disclose employee training programs (95% and 84%, respectively), with the majority of S&P 500 and S&P 400 companies holding such training at least annually.
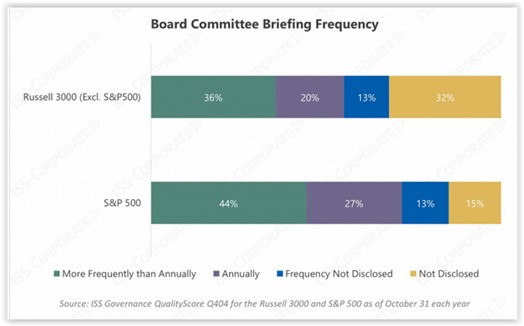
Board committee briefings (Q404)
- More than 70% of S&P 500 companies and more than half of R3000 companies disclose briefing their boards on cybersecurity issues at least annually.
Information security expertise on the board (Q405)
- While just 10% of S&P 500 companies disclose no directors with cybersecurity experience or expertise, that compares to 41% of R3000 companies. ISS considers a director to have information security skills if they have any current or previous employment with companies in information security or relevant industries, current or previous employment positions relevant to information security, certifications in information security or similar, or explicit disclosure of information security expertise.
Supply chain cyber risk management (Q462)
- The vast majority of S&P 500 and R3000 companies (81% and 76%, respectively) disclose a formal supply chain/third-party cyber risk management program.
- Nearly one-quarter of S&P 500 companies and nearly 20% of R3000 companies disclose having established a framework and process for determining the materiality of information security events.